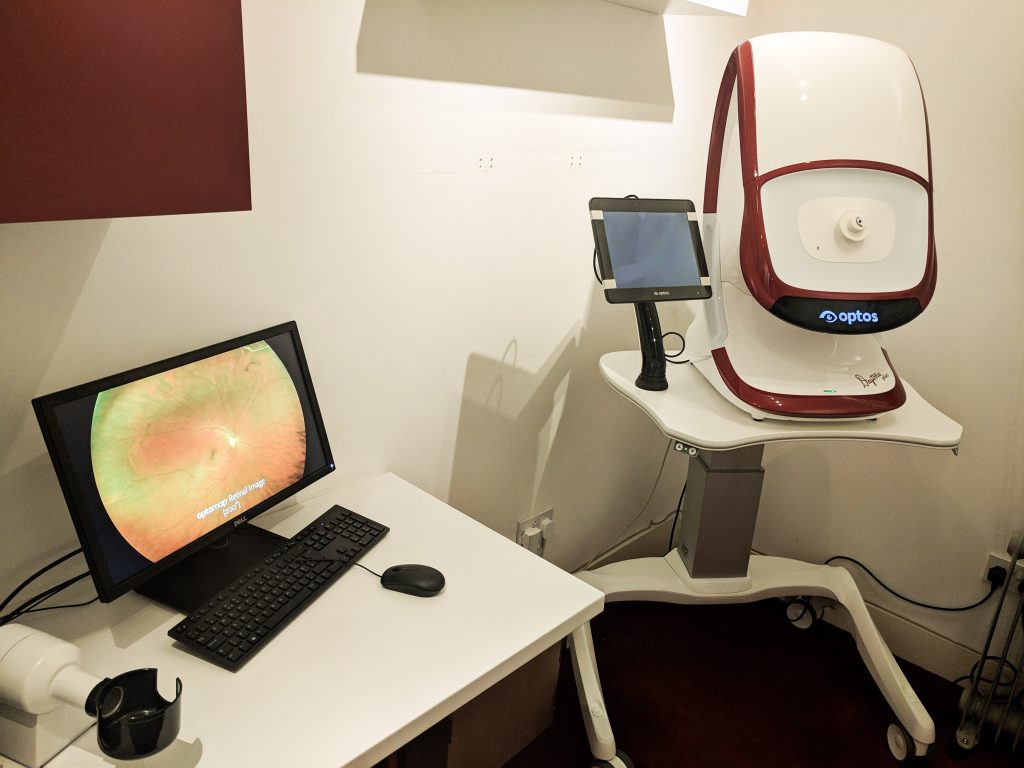
Optomap by Optos, (especially the latest Daytona plus) is the worlds most advanced, widest and comprehensive scan of your retina at the back of your eyes. It can capture a breathtaking image in just a few seconds, in order to ensure that the back of your eyes are healthy and reduce the risk of retinal problems and blindness
What is an Optomap machine?
Optomap is a highly advanced device that takes a detailed and comprehensive image of the retina at the back of the eye. It takes the widest image possible compared to all other devices in the world. It's completely safe, painless and takes seconds to get an image. It was designed by an engineer who's son lost his sight because of a tear in the retina that couldn't have been detected using existing technology, He founded Optos the company that make the device.
How does it work?
The machine has a special safe, low powered laser combined with an accurately curved mirror to look through your pupil and scan your retina to create a detailed image.
What is the retina?
The retina is an extremely thin layer, inside the back of the eye, that senses the light entering your eye to form an image. It acts very similarly to the film or sensor in a camera in the way it captures the light. In many retinal diseases, you may not notice any changes until it is too late. An eye test should always include an examination of the retina to check for problems and risks of blindness. The retina is the only place in your body where we can see live blood vessels, so many conditions that affect the blood supply, such as diabetes and high blood pressure may be seen in the retina (see more below)
Is it safe to use the Optomap device, are there any risks or dangers?
It is completely safe. The device has been tested rigorously in Europe to achieve a CE certification and approved by the US FDA (food and drug administration). There are no risks or dangers to the eye.
How long does it take to scan the eyes?
The entire process takes about 5 minutes. Each Optomap scan only takes a few seconds. We take a couple of different scans for each eye to ensure we have a detailed and useful image.
Is dilation of the pupils necessary?
The beauty of the optomap is that, in most cases, dilation of the pupils is not necessary. Unlike existing technology and examination techniques, we can get a good image if you have small pupils. This means no stinging eye drops or blurry vision for a few hours.
Is it worth having an Optomap scan?
Everyone should have a scan at their routine sight test. We can examine over 4 times as much of the retina compared to all other techniques. Without it we would never know if there are potential problems to address if we only examine your eyes with conventional methods. It should be an essential part of every sight and eye test.
How much does it cost to examine my retina?
An Optomap scan costs £40, this is far less than the cost of missing a serious problem with your eyes
Are there any specific reasons to have an optomap image?
There are certain conditions where an optomap will be essential to assess signs of potential issues that could threaten your sight:
- High myopia/short sight
- Retinal detachment
- Retinal tears
- Floaters
- Choroidal naevus
- Toxoplasmosis scars
- Diabetes
- Macula degeneration
- Hypertension/high blood pressure
- Hydroxychloroquine users
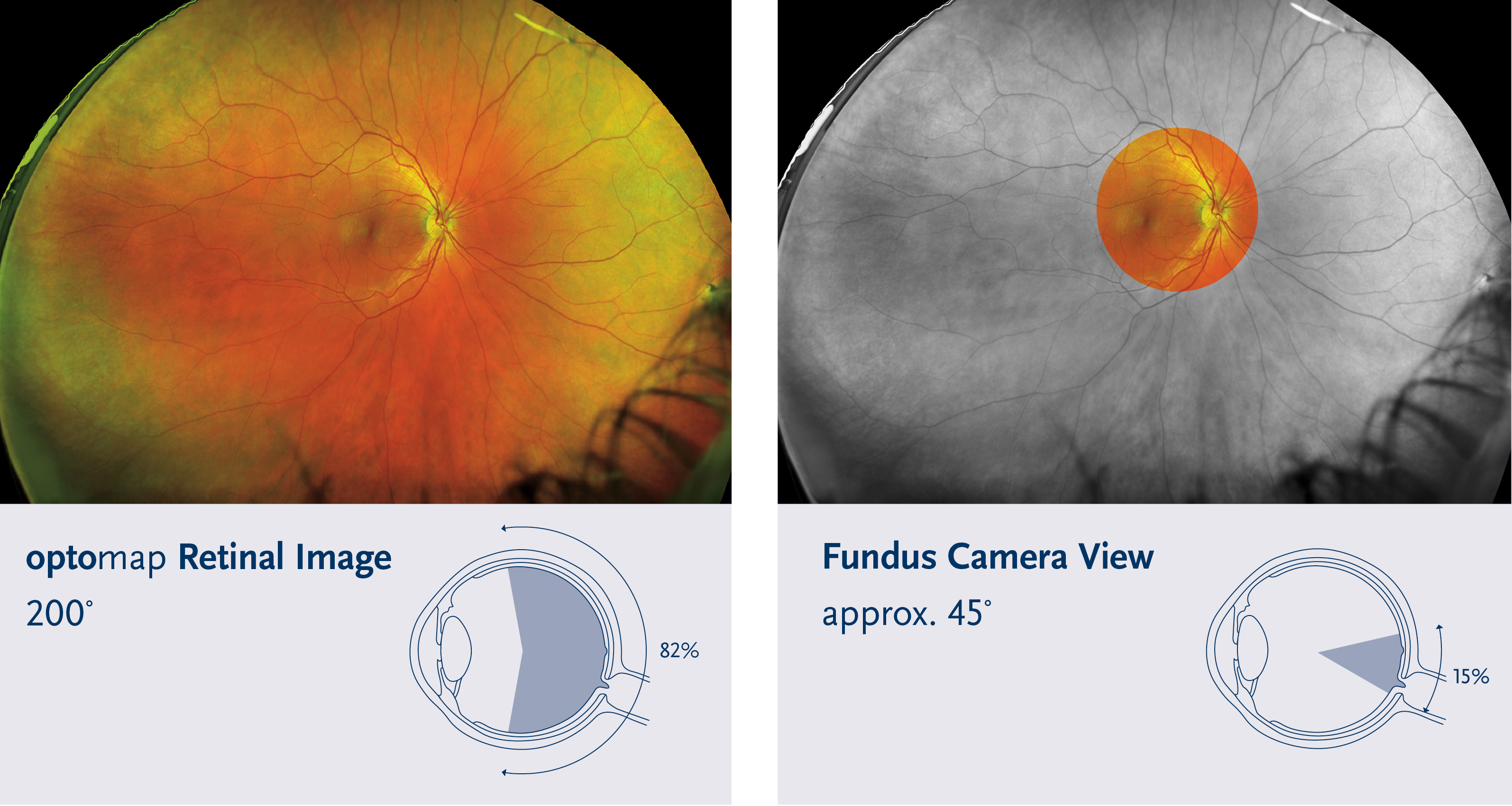
What is Ultra widefield?
Normal examinations of the retina can only see about 15-30% of the retina. With the optomap, we can see over 80% of the retina in a single image. This means that the about we can see of your retina is nearly 3 times more with a significantly wider (ultra-wide) image. See the difference between existing technology and an Optomap image below:
Why is it better than existing methods and technology?
Existing technologies have well-known limitations.
- Area of retina that can be examined is limited
- Need for Dilation
- Speed taking a reliable image can be slow
- Existing technology takes training and more operator skill
- Older technology is difficult to use with children
- It can take time to capture or view the image
See the huge difference in image view between an existing device and the Optomap below:
What do the images look like?
How do you analyse the optomap images?
We start by looking at the optic nerve. The circle shaped structure near the centre of the image. It has blood vessels coming out through here. We check the appearance of the nerves and blood vessels. Then we check an area of the retina called the macula. This is the region where the fine and detailed vision is detected by the eye. After this we analyse the more peripheral areas of the retina for damage, scarring, wear and tear or risks of other conditions of the eye.
Can I have a copy of my images?
Of course, we will email you a copy